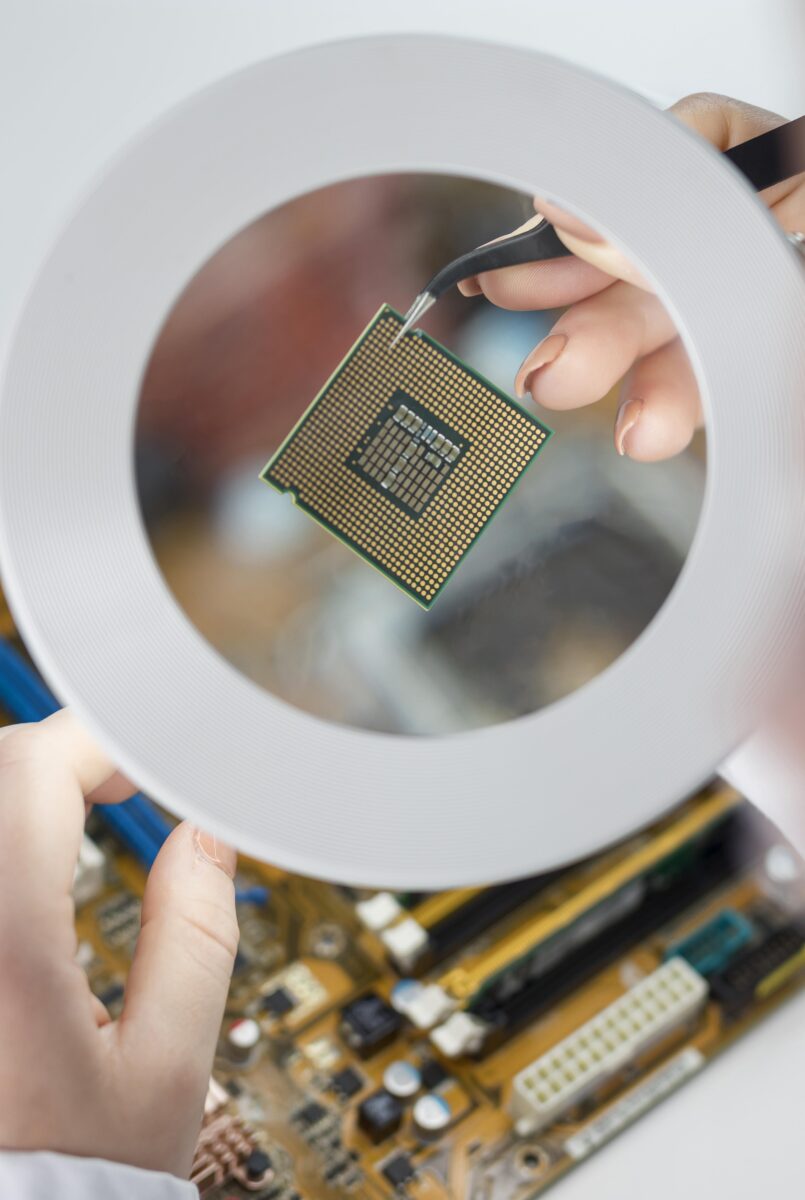
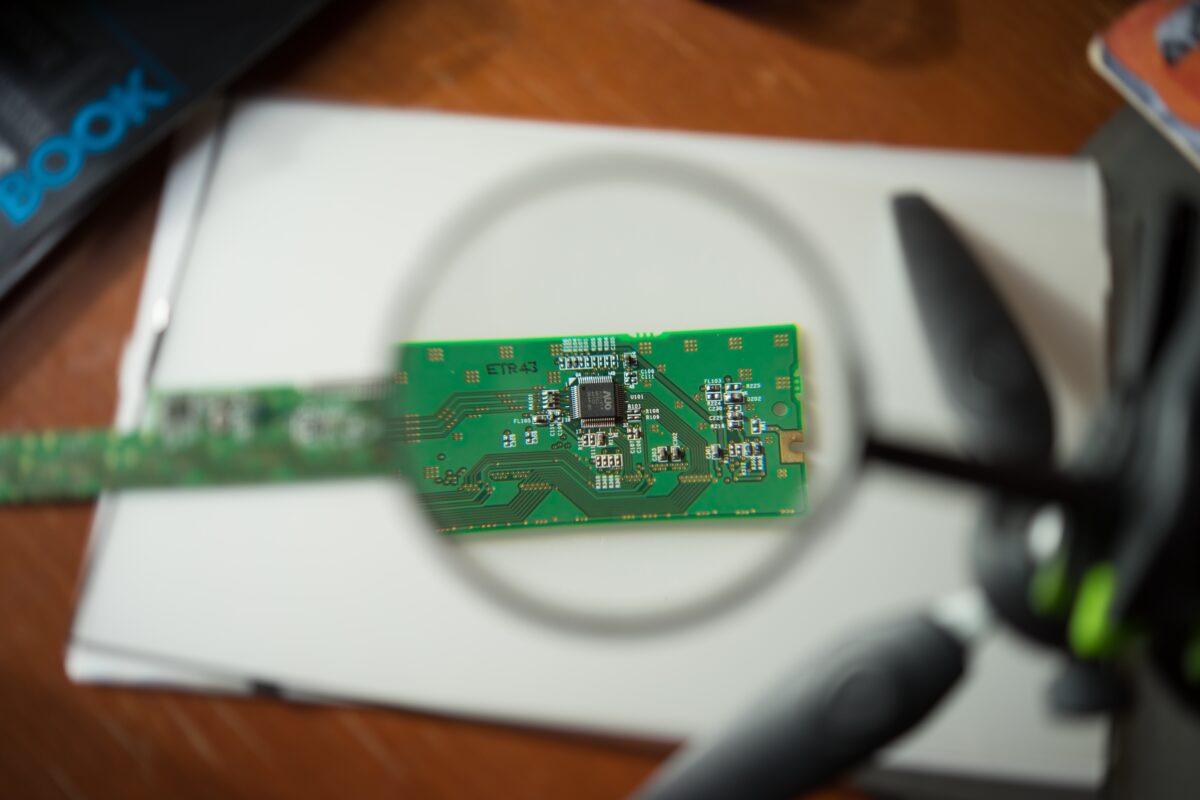
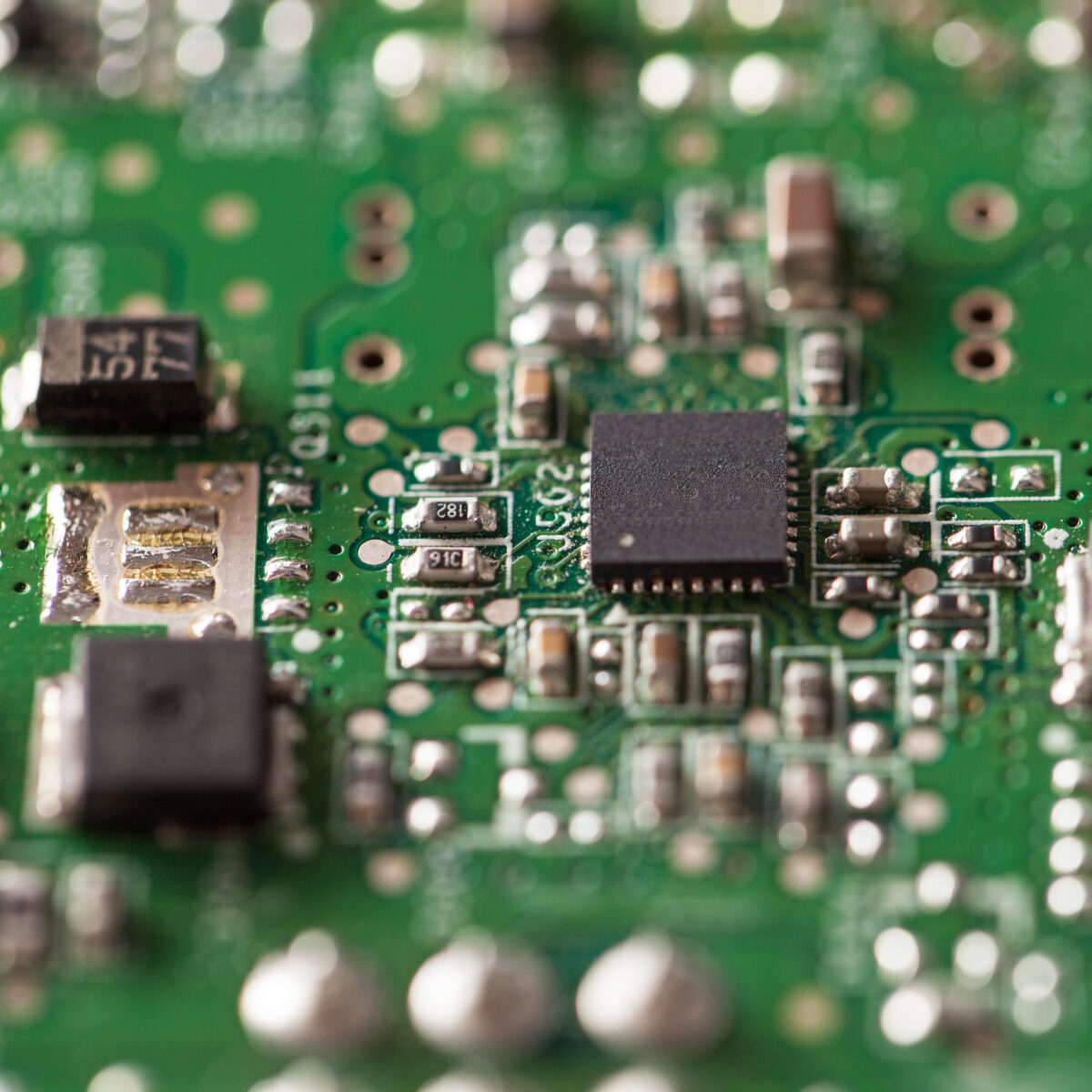
How to Conduct a Visual Inspection: A Step-by-Step Guide
Though no method is perfect, a thorough visual inspection is a powerful tool for detecting counterfeit components. It can significantly increase your chances of identifying suspect parts before they cause problems. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you conduct your own inspection:
Start with the Markings:
Fonts: Review the font used for component markings. Ensure it aligns with the manufacturer’s standard font, as counterfeits often display blurry, mismatched, or irregular fonts. Pay attention to inconsistencies in kerning (the spacing between letters) and stroke weight.
Part Numbers: Check the part number against the manufacturer’s datasheet or official website. Look for any discrepancies, misspellings, or illogical character combinations.
Inspect for Physical Imperfections:
Solder Joints: Inspect the solder joints for quality and consistency. Counterfeit components frequently exhibit uneven, poorly applied, or excessive solder. Look for evidence of rework or re-balling, where the component’s leads have been resoldered.
Color Variations: Authentic components generally exhibit consistent color shades within a batch. Inconsistencies, discoloration, or blotches may suggest the use of inferior materials or remanufactured parts.
Molding Imperfections: Examine the component body for visible seams, burrs, or uneven surfaces. These imperfections indicate substandard or rushed manufacturing processes, which are often associated with counterfeit operations.
Physical Damage: Inspect the component for any cracks, chips, or scratches. While physical damage is not always a sign of counterfeiting, it may affect performance or suggest mishandling.
Examine the Leads and Pins:
Don’t Forget the Packaging:
Unauthentic or Damaged Packaging: Original component packaging is typically high quality and free from damage. Flimsy, low-quality packaging, or packaging with inconsistent branding, could be a sign of a counterfeit.
Blurry or Unclear Labels: Labels on authentic components are clear, readable, and provide accurate information. Blurry or indistinct printing may indicate counterfeiting.
Excessive or Uneven Glue Application: Check for signs of excessive or uneven glue application, which can be a quick tactic used by counterfeiters to repackage or relabel components.
Compare to Datasheets and Known Samples:
Datasheet verification: Always compare the component’s physical appearance and markings to the manufacturer’s official datasheet for detailed specifications that can help you identify discrepancies.
Known samples: If you have access to authentic samples of the same component, compare them side-by-side, looking for any differences in markings, physical appearance, or construction.
Beyond Visual Inspection: Other Counterfeit Detection Methods
Although visual inspection is a valuable tool, it isn’t always definitive. If you have concerns that a component may be counterfeit after a visual inspection, consider these additional methods:
![]()
Electrical Testing
Assess the electrical parameters of the component and compare them to the manufacturer’s specifications. Significant deviations may indicate that the component is counterfeit.
![]()
X-ray Analysis
X-ray inspection can uncover internal defects, construction inconsistencies, and signs of tampering that are not visible to the naked eye.
![]()
Chemical Analysis
This technique can identify the materials used in the component and detect the presence of any substandard or unauthorized materials.
![]()
Traceability and Documentation
Confirm the component’s origin and chain of custody by examining the supplier’s documentation and certifications.
![]()
IC Decapsulation
This involves removing the packaging of an integrated circuit (IC) to examine the die and internal structure. It can reveal inconsistencies in design, markings, or construction that may indicate counterfeiting.
![]()
Solderability Test
This test assesses the component’s ability to be soldered properly. Counterfeit components may have poor solderability due to the use of inferior materials or improper surface finishes.
Suntsu: Your Partner in Quality and Authenticity
At Suntsu, we are dedicated to providing our customers with high-quality, authentic electronic components. We have implemented rigorous quality control processes to ensure that all components meet the highest standards of authenticity and reliability.
Our extensive global sourcing network and strong partnerships with authorized manufacturers help us reduce the risk of counterfeit components entering our supply chain. We also provide a variety of value-added services, such as counterfeit mitigation programs and expert engineering support, to assist our customers in safeguarding their businesses against the threat of counterfeits.
Don’t let counterfeits compromise your products and your reputation. Contact Suntsu today to learn more about our commitment to quality and how we can help you secure authentic electronic components for your business.